AI task sequencing is transforming financial operations by autonomously managing workflows, optimizing processes, and handling unstructured data like emails and contracts. However, most companies struggle to achieve measurable returns on their AI investments - 95% report no ROI, and the median ROI in finance is just 10%. For CFOs, the focus should be on redesigning workflows and linking AI use cases to deliver results.
Key takeaways:
- AI task sequencing: Automates multi-step workflows, improving efficiency and cutting costs.
- Challenges: Low ROI, inefficiencies, data issues, and "pilot traps."
- Solutions: Redesign workflows, focus on measurable KPIs, and adopt sprint-based implementation.
- Results: Companies using integrated AI strategies see faster budgeting (33% reduction) and significant cost savings (up to 16%).
The bottom line: AI can deliver real value, but success depends on rethinking workflows and linking AI use cases strategically.
ROI Challenges in AI Task Sequencing
The ROI Gap in AI Investments
Organizations are pouring an estimated $30–$40 billion annually into generative AI, yet a staggering 95% report no measurable returns. Only 39% have seen any EBIT impact, even though 88% claim regular AI usage. The numbers don’t get much better in finance: the median ROI for AI initiatives is just 10%, far below the 20% many finance leaders aim for. To make matters worse, the typical payback period for AI investments is 2–4 years - much longer than the 7–12 months expected for standard tech investments. It’s no surprise, then, that only 45% of finance executives can quantify the ROI of their AI efforts.
Why the struggle? AI doesn’t follow the straightforward "problem-solution-result" formula we see with traditional software. Instead, it’s a process of trial and error, where success depends on factors like model reliability, employee buy-in, and adaptability within the organization. This unpredictability is a key reason why many companies fail to see the returns they expect, especially when it comes to task sequencing.
Why Task Sequencing Fails to Deliver Results
The challenges of ROI are amplified by missteps in task sequencing, which often undermine AI’s potential. One major issue is that many organizations try to integrate AI into existing workflows without rethinking or redesigning them. High-performing companies, however, are three times more likely to completely overhaul workflows to make them AI-compatible. As Michael Chui, Senior Fellow at McKinsey, puts it:
"The value of AI comes from rewiring how companies run... the redesign of workflows has the biggest effect on an organization's ability to see EBIT impact."
Another problem is the inefficiency caused by excessive verification. Employees often spend too much time double-checking AI outputs, especially when those outputs are confidently wrong. This extra layer of scrutiny can wipe out any productivity gains. Boston Consulting Group highlights this issue:
"If you still need to verify GenAI-generated output line by line, the efficiency gains evaporate."
Beyond workflow redesign and verification challenges, many organizations lack the necessary data infrastructure for AI to thrive. Gaps in data quality and accessibility prevent AI systems from making effective, real-time decisions. Companies often invest in AI tools before addressing these foundational data issues, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
Lastly, many businesses fall into the "pilot trap" - running small-scale experiments without scaling AI across the enterprise. About two-thirds of companies remain stuck in this phase. Lower-performing teams tend to spread their efforts thin, tackling an average of 6.1 use cases. In contrast, high performers focus on just 3.5 use cases, choosing depth over breadth for greater impact.
Strategies for Better AI Task Sequencing
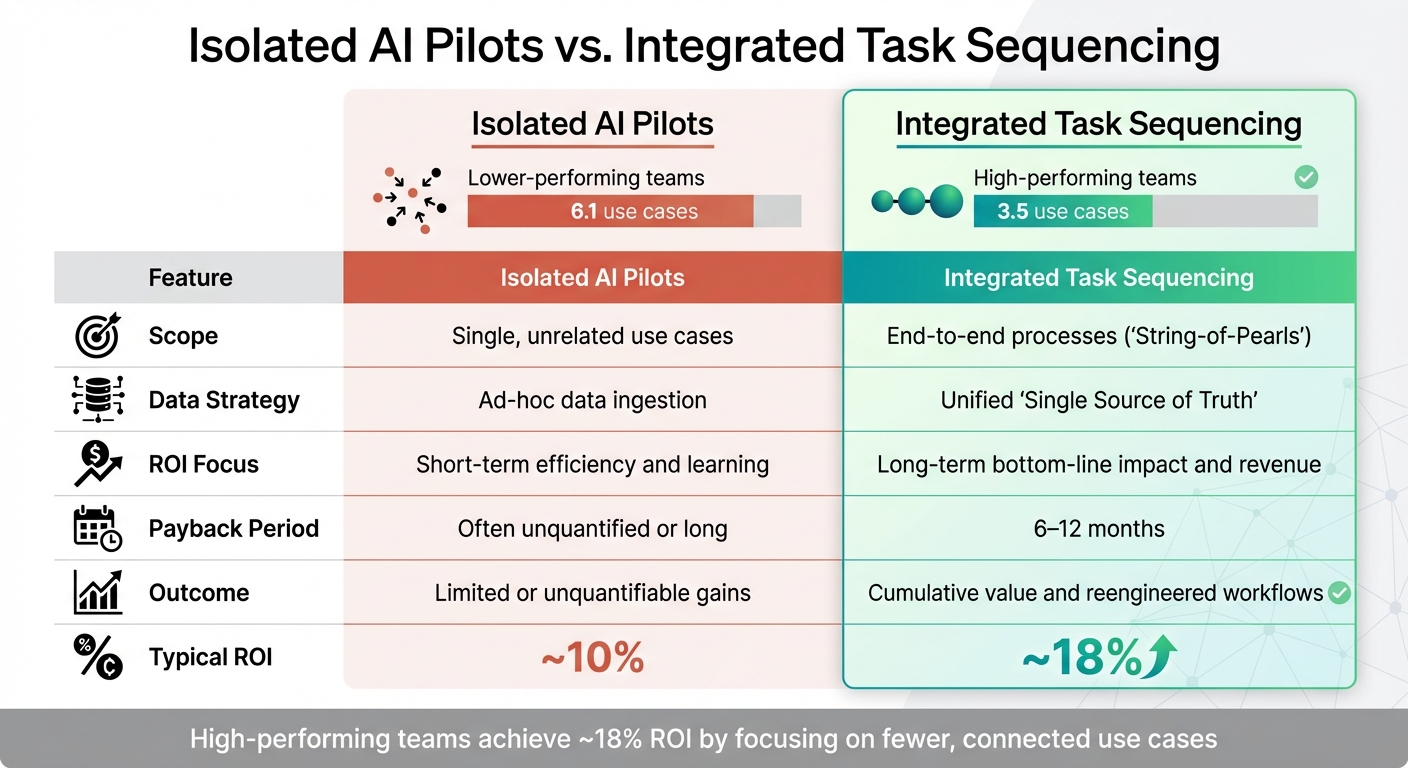
Isolated AI Pilots vs Integrated Task Sequencing: ROI Comparison
Moving from Isolated Pilots to Integrated Workflows
Bridging the ROI gap in AI implementation requires more than just integration - it demands a complete overhaul of workflows. The distinction between isolated AI pilots and integrated task sequencing lies in how projects are built and executed. Isolated pilots treat each use case as a standalone project, with separate processes for data ingestion, modeling, and validation. In contrast, integrated workflows follow a "String-of-Pearls" approach, linking connected use cases to generate cumulative value from investments.
The difference in outcomes is striking. Teams that focus on a few high-impact use cases often achieve a return of around 18%, while those spreading efforts thin across multiple projects typically struggle to exceed a 10% return.
| Feature | Isolated AI Pilots | Integrated Task Sequencing |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Single, unrelated use cases | End-to-end processes ("String-of-Pearls") |
| Data Strategy | Ad-hoc data ingestion | Unified "Single Source of Truth" |
| ROI Focus | Short-term efficiency and learning | Long-term bottom-line impact and revenue |
| Payback Period | Often unquantified or long | 6–12 months |
| Outcome | Limited or unquantifiable gains | Cumulative value and reengineered workflows |
Take, for example, a consumer goods company that revamped its FP&A department by introducing a driver-tree model paired with a generative AI interface. This transformation led to a 50% reduction in the time needed to generate reports and accelerated forecast delivery by 30%. This success highlights the potential of redesigning workflows from the ground up, rather than simply layering AI on top of outdated systems. Such an approach naturally paves the way for meaningful, measurable results.
Redesigning Workflows for Measurable Impact
Integrated workflows are only the beginning; for real, measurable impact, a complete workflow redesign is essential. This isn’t about minor improvements to existing processes - it’s about reimagining entire systems to unlock new possibilities. As noted earlier, redesigning workflows has the most significant impact on an organization's ability to achieve EBIT gains.
Start by adopting a driver-tree model. This framework mathematically links operational metrics from various data sources to financial outcomes, enabling AI to calculate the bottom-line impact of specific actions. For example, a global pharmaceutical company used AI-powered contract intelligence to enforce commercial terms across more than 250,000 supplier contracts in 17 languages, resulting in annual savings of $70 million.
Next, establish clear KPIs and accountability before diving into development. Define the current costs in terms of hours, dollars, and full-time equivalents (FTEs), set target costs, and determine the break-even timeline. Assign specific individuals to own these metrics - without this accountability, initiatives risk becoming experiments instead of true transformations.
Finally, incorporate human-in-the-loop controls to maintain oversight and ensure continuous improvement. AI agents should flag anomalies for human review, and these corrections should feed back into the model, creating a cycle of ongoing refinement. This approach also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements by maintaining clear governance and audit trails.
Robin Washington, President and COO at Salesforce, captures the essence of this shift:
"The introduction of digital labor isn't just a technical upgrade - it represents a decisive and strategic shift for CFOs. With AI agents, we're not merely transforming business models; we're fundamentally reshaping the entire scope of the CFO function."
This mindset is critical for CFOs and other leaders: the goal isn’t incremental efficiency but a complete redesign that delivers measurable, transformative outcomes.
Use Cases for AI Task Sequencing in Finance
Accounts Payable Automation
Finance teams are taking automation to the next level by using AI to handle multi-step accounts payable (AP) workflows. Instead of relying on basic AI assistance, companies are embracing full automation. AI task sequencing enables straight-through processing, which means invoices are captured, data is classified, purchase orders are matched, tolerance rules are applied, and entries are auto-approved - all without human intervention.
The results speak for themselves. Companies that invest at least 20% of their IT budgets in automation have reduced annual AP costs per invoice by 25% and achieved 22% overall cost savings. Additionally, AI systems that verify contract compliance have uncovered value leakage equal to about 4% of total spending. These systems help recover missed early payment discounts and correct misapplied tiered pricing terms.
Bain & Company emphasizes the importance of focusing on tangible results:
"The goal isn't better spreadsheets; it's measurable gains in touchless processing, faster cycle times, and more effective control."
To achieve these outcomes, companies need to combine technologies effectively. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can handle rule-based tasks, while Generative AI (GenAI) is better suited for reading and interpreting complex, unstructured contracts in multiple languages. A solid foundation is also essential - clean vendor records, standardized charts of accounts, and clear policies provide the context AI needs to perform effectively.
These advancements show how AI task sequencing can transform finance operations into streamlined, results-driven systems.
Financial Planning and Forecasting
AI isn't just changing transactional workflows - it’s also revolutionizing financial planning and forecasting. By automating data-heavy processes, AI task sequencing accelerates decision-making and improves accuracy. Companies that have embraced AI report a 33% reduction in annual budget cycles, a 50% decrease in report generation time, and forecasts delivered 30% faster. This enables finance teams to shift their focus to more strategic activities.
High-performing teams are taking this further by integrating connected use cases. For example, they start with data-driven reporting models that lay the groundwork for algorithmic forecasting. These models are then enhanced with dynamic scenario modeling, creating workflows that link operational metrics to financial outcomes. This approach not only speeds up processes but also delivers meaningful insights.
The benefits go beyond efficiency. Companies with advanced AI adoption have redirected 30% of their resources to high-value tasks, compared to only 10% for organizations lagging behind. Finance professionals in these companies also spend 20% to 30% less time on data crunching, freeing them up for analysis and strategic planning.
A hybrid approach combining traditional AI and Generative AI has proven particularly effective. While traditional AI handles deterministic forecasting, Generative AI is used for probabilistic tasks like drafting variance explanations and narrative commentary. This blend of technologies ensures both accuracy and efficiency while maintaining compliance with regulations such as SOX and IFRS.
These examples highlight how AI task sequencing not only enhances efficiency but also enables finance teams to deliver greater strategic value.
Risk Monitoring and Compliance
AI is also reshaping how finance teams manage risk and compliance. With AI task sequencing, companies can monitor financial risks and compliance in real time. Currently, 45% of CFOs use AI for continuous monitoring of working capital and cash flows, and adoption is growing as these systems prove their ability to detect anomalies and fraud.
For example, AI can sequence the processing of contracts and invoices to ensure terms like early payment discounts, volume rebates, and tiered pricing are correctly applied. This prevents value leakage that often goes unnoticed during manual reviews. Additionally, 60% of CFOs are open to using autonomous AI for adapting financial functions to new regulations, while 58% are willing to let AI handle compliance reporting and filings.
AI task sequencing also enhances data governance and audit readiness by standardizing account charts and intercompany transactions. It coordinates workflows across systems like ERP, AP, and treasury, exposing policy exceptions and control failures.
However, successful implementation requires careful planning. Over half of organizations using AI (51%) have encountered negative outcomes, with 30% reporting issues related to AI inaccuracy. To mitigate these risks, companies must establish governance frameworks upfront, focusing on risk management, explainability, and compliance. High-performing organizations are three times more likely to redesign workflows to fully leverage AI’s potential rather than simply adding it to existing processes.
These use cases illustrate how AI task sequencing can transform risk and compliance functions, making them more efficient and effective while reducing operational risks.
sbb-itb-34a8e9f
Measuring and Tracking ROI from AI Task Sequencing
Creating an ROI Charter for Task Sequencing
CFOs play a crucial role in ensuring the success of AI task sequencing by establishing a clear ROI charter. This document outlines the expected outcomes, assigns ownership, defines metrics, and sets timelines, creating a solid foundation for implementation. Without this level of planning, AI initiatives often fall into the 95% of enterprise projects that fail to deliver measurable results.
Start by recording baseline KPIs such as processing times, error rates, cost per transaction, and revenue per completion. For example, Chobani achieved a 75% reduction in expense processing time after documenting its baseline metrics and implementing AI-powered tools within SAP Concur.
When building the ROI charter, CFOs should focus on 3–5 KPIs that directly align with primary business goals. These might include efficiency improvements (e.g., hours saved), revenue growth (e.g., conversion rates), or risk mitigation (e.g., fewer incidents). To meet reporting standards, translate these KPI improvements into financial terms using metrics like Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and payback periods.
"Value concentrates where organizations wire AI into processes with explicit ownership and measurement".
Without this structured approach, AI investments risk becoming disconnected from tangible business outcomes. A well-defined ROI charter not only grounds AI initiatives but also sets the stage for rapid and disciplined implementation.
Sprint-Based Implementation for Faster Results
Once the ROI charter is in place, a sprint-based implementation can quickly move AI projects from pilot phases to full-scale production. Using a 90-day operating model, initiatives progress through three key phases:
- Week 1: Establish baselines and finalize the ROI charter.
- Weeks 2–4: Run AI systems in shadow mode, where they operate alongside existing human processes but do not yet impact customers.
- Days 30–90: Transition to guarded autonomy, where AI begins to take on operational tasks.
This structured approach has delivered impressive results. For example, Microsoft reduced manual planning efforts by 50% and improved on-time planning by 75% through disciplined implementation. Similarly, SA Power Networks saved $1 million in a year by deploying an AI-powered application in phases, achieving a 99% success rate in identifying corroding infrastructure poles.
HRbrain’s Workflow Transformation Sprint offers another example of this methodology in action. Over just three weeks, the program redesigns two workflows end-to-end, complete with implementation details, operating playbooks, and adoption systems - all tied back to clear KPIs. For organizations needing even faster results, the 5-day ROI Reset Sprint evaluates all AI initiatives, categorizing them into Stop, Start, or Scale decisions, and creates a 30-day plan to deploy one workflow into production.
To ensure long-term value, reinvest productivity gains into higher-value tasks. As Jatin Dalal, CFO of Cognizant, explains:
"The productivity gains from AI investment must be reinvested into higher‐value work to compound long‐term value".
Without a strategy to redirect reclaimed hours into strategic initiatives, efficiency improvements may fail to drive sustainable growth.
Finally, sprint-based implementations should include a kill switch to manage risks effectively. This feature allows for a quick rollback if needed, supported by predefined communication templates, clear ownership, and multiple layers of failure prevention. With these safeguards, CFOs can confidently accelerate AI adoption while maintaining control over outcomes.
Conclusion
A staggering 95% of enterprise AI initiatives fail to deliver measurable returns, with the median ROI in finance sitting at just 10% - far below the 20% many leaders aim for. The problem isn’t the technology itself but how it’s deployed.
Forward-thinking CFOs are adopting a "string-of-pearls" strategy, which links related use cases and focuses on business-critical areas like risk management and forecasting. This approach embodies the guiding principle:
"Make ROI the strategy - and lead from there".
This connected strategy sets the stage for the next chapter: agentic AI. Agentic AI, designed to autonomously manage complex workflows, is on the horizon. In fact, 75% of finance leaders predict it will become commonplace within three years, and CFOs are already allocating 25% of their AI budgets toward this emerging technology. Partnering with external experts has proven to be a game-changer, with organizations seeing a 67% success rate compared to just 33% for internal builds. This highlights the importance of collaboration with specialists.
However, the true key to unlocking AI’s potential lies in rethinking workflows from the ground up. Without a complete overhaul, even the most advanced AI tools will struggle to deliver. High-performing organizations are 2.8 times more likely to have fully redesigned their workflows. The real value of AI emerges when technology investments are paired with the human factors - skills, trust, and the time needed to adapt.
If your AI initiatives aren’t delivering, it might be time to hit reset. HRbrain offers solutions tailored to drive results. Their 5-day ROI Reset Sprint ($9,500–$12,500) provides a comprehensive audit of AI spending, identifies Stop/Start/Scale decisions for each project, and delivers a 30-day plan to get one workflow into production. For a deeper overhaul, the 3-week Workflow Transformation Sprint ($18,000–$28,000) redesigns two workflows end-to-end, complete with implementation specs, operating playbooks, and systems to ensure immediate execution.
The bottom line? Redesigning workflows isn’t optional - it’s essential for turning AI investments into measurable outcomes. Can you afford to wait?
FAQs
How can CFOs optimize workflows to maximize AI ROI in task sequencing?
To get the most out of AI investments, CFOs should think beyond automating isolated tasks. Instead, the focus should be on weaving AI into entire workflows. This approach allows AI to boost productivity across processes, leading to measurable results and long-term value.
The process starts with pinpointing use cases that have the potential for significant impact. From there, collaboration across teams ensures everyone is on the same page, and automation can be scaled step by step. By embedding AI into the core of operations and building systems that can adapt and evolve, companies stand to improve efficiency, cut costs, and unlock meaningful financial gains.
What challenges do companies face when using AI for task sequencing in finance?
Many businesses face difficulties in achieving solid outcomes when using AI for task sequencing in finance. One major hurdle? Moving beyond the pilot phase. Research indicates that a staggering 95% of AI projects fail to produce measurable returns. This often stems from poor integration of AI tools into existing workflows or a lack of alignment with overarching business objectives.
Other challenges include skepticism from employees who might not trust AI with critical tasks, lengthy adoption timelines that can drag on for months, and excessive spending on tools without clear metrics for success. To overcome these obstacles, companies need to rethink their workflows, weave AI into their decision-making processes, and establish clear accountability for results.
What makes integrated task sequencing more effective than standalone AI pilots?
Integrated task sequencing is all about weaving AI into end-to-end workflows that are designed to consistently deliver measurable returns. Unlike isolated AI projects that often function independently and struggle to connect with essential business operations, this method ensures AI becomes a seamless part of everyday processes, delivering lasting impact and value.
The focus here is on rethinking workflows, governance structures, and accountability systems to make sure AI investments lead to real, measurable outcomes. By emphasizing clear KPIs and scalability, integrated task sequencing helps organizations sidestep common challenges like low adoption rates or the inability to track meaningful results.